
Over time, air conditioning units can wear out, resulting in reduced efficiency and performance. While regular maintenance can extend the life of an AC system, there are specific signs that indicate it may be time for a full replacement. Below is a list of key indicators to watch for before your system fails completely.
1. Frequent and Costly Repairs
If you find yourself calling for professional repairs multiple times a year, it may not make financial sense to keep your current unit. Over time, the cost of continual repairs can add up significantly. Replacing an aging system is often more cost-effective than repairing it repeatedly.
- Example: A compressor that fails frequently or refrigerant leaks that require multiple refills signal underlying issues.
- Rule of Thumb: If repair costs exceed 50% of the unit’s value, replacement is recommended.
2. Inefficiency and Higher Energy Bills
Older systems often require more energy to deliver the same cooling power as newer models. Rising utility bills without increased usage are a strong indicator that your AC is no longer operating at optimal efficiency.
| Feature | Older Units (10+ Years) | Newer Units (with SEER > 16) |
| Energy Efficiency Ratio | Low | High |
| Operating Costs | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Significant | Reduced |
Consider upgrading to an energy-efficient system with advanced technology to save on monthly costs.
3. Inconsistent Cooling
An air conditioner should provide consistent temperatures throughout your home or office. If certain rooms feel too warm while others are too cold, it could indicate failing components such as the blower motor or evaporator coil.
Common causes of inconsistent cooling:
– Ductwork issues or blockages
– Aging thermostat sensors
– Insufficient refrigerant levels
Replacing your AC may resolve these problems when repairs fail to restore consistency in comfort levels.
4. Unusual Noises or Odors
Strange noises like grinding, rattling, or squealing often point to mechanical failure, while musty odors suggest mold or mildew buildup inside the system. These signs not only affect performance but could also impact indoor air quality negatively.
Key Sounds and Their Potential Causes:
– Humming: Electrical issues within the motor – Banging: Loose internal parts – Whistling: Airflow blockages
If professional cleaning doesn’t resolve these issues, replacement may be required.
5. System Age Exceeds Expected Lifespan
The average lifespan of an AC unit is approximately 10–15 years with routine maintenance. Once your system surpasses this timeline, its components will begin to fail more frequently due to natural wear and tear.
Signs associated with old age include: – Reduced efficiency despite tune-ups – Difficulty maintaining desired temperature settings – Increased likelihood of refrigerant leaks
Investing in a modern unit ensures better performance and takes advantage of technological advancements like smart thermostats and eco-friendly refrigerants.
Key Takeaway from a Leading HVAC Company Orlando, FL
Recognizing these five indicators early can help you avoid sudden breakdowns during peak seasons when reliable cooling is crucial. While repairs might provide temporary solutions, understanding when replacement becomes inevitable ensures greater comfort, safety, and energy savings over time.
The Tools HVAC Technicians Use to Diagnose and Fix Air Conditioning Systems Effectively
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technicians rely on a variety of specialized tools to diagnose and repair air conditioning systems with precision. These tools are essential for identifying issues, ensuring optimal performance, and extending the lifespan of AC units. Below is an exploration of some key tools used by professionals in this field.
Diagnostic Tools for Identifying Problems
- Measure refrigerant pressure in the system.
- Help identify leaks or improper refrigerant levels that can compromise cooling efficiency.
- Monitor air intake and output temperatures to assess temperature differentials.
- Useful in determining whether the system is cooling effectively.
- Test electrical components such as relays, capacitors, and wiring connections for faults or power inconsistencies.
- Ensure safe operation by detecting potential electrical hazards.
- Essential for detecting refrigerant leaks that can cause energy inefficiency or environmental harm.
Repair and Maintenance Tools
- Remove air, moisture, or contaminants from refrigeration lines before adding fresh refrigerant during repairs or installations.
- Allow technicians to connect directly to the refrigerant lines for charging, recovering, or diagnosing issues with pressure readings.
- Includes brushes and chemical sprays for cleaning evaporator and condenser coils to enhance airflow efficiency.
- Used to straighten bent condenser fins that might block airflow and reduce overall system performance.
- Essential for dismantling parts such as panels or fasteners during inspections and repairs.
Advanced Technology Utilized by HVAC Technicians
- Detect heat signatures in ducts or components to identify insulation issues or airflow blockages efficiently.
- Smartphone-enabled devices are becoming increasingly popular among technicians.
- These tools use apps to measure airflow rates, temperatures, humidity levels, etc., offering real-time data analysis.
- Measure the velocity of air passing through ducts and vents to ensure balanced distribution throughout a building.
| Tool Type | Function |
| Refrigerant Gauges | Monitors pressure levels |
| Leak Detectors | Identifies refrigerant leaks |
| Vacuum Pumps | Removes moisture/air from systems |
| Smart Diagnostic Tools | Provides real-time data through connected apps |
| Coil Cleaning Brushes/Tools | Cleans coils for better airflow |
Safety Equipment Used Alongside Tools
- Protective gloves: Shield hands from sharp edges or chemicals.
- Safety goggles: Prevent eye injuries during coil cleaning or chemical handling.
- Respirators: Protect against inhaling harmful gases released during repairs.
By combining traditional hand tools with advanced diagnostic equipment, HVAC professionals efficiently manage everything from routine maintenance tasks to complex repairs while adhering to safety protocols at every step of the process. This blend of expertise and technology ensures reliable service delivery in any situation involving air conditioning systems.
Exploring What HVAC Technicians Actually Do Every Day in the World of AC Service
HVAC technicians play an essential role in maintaining comfortable and energy-efficient living and working environments. Their daily responsibilities encompass a broad range of tasks, from diagnostic evaluations to implementing repairs or replacements, ensuring that air conditioning systems function optimally. Below is an overview of the key activities HVAC technicians engage in during their typical workday.
Routine Inspections and Maintenance
- Check refrigerant levels: Low refrigerant can indicate leaks or inefficiencies.
- Inspect coils: Evaporator and condenser coils are cleaned to maintain performance.
- Examine electrical components: Faulty wiring or damaged capacitors can impair operation.
- Inspect filters: Dirty or clogged filters reduce airflow, increasing strain on the system.
- Lubricate moving parts: Proper lubrication minimizes wear and tear on motors and fans.
These preventative measures help prolong the lifespan of air conditioning systems while reducing energy consumption.
Diagnosing System Failures
- Using digital multimeters to measure voltage and continuity in electrical circuits.
- Testing refrigerant pressure with specialized gauges to detect leaks or overcharging.
- Inspecting thermostats for calibration errors or connectivity problems.
- Running system tests to assess airflow rates and temperature differentials.
By systematically troubleshooting each component, technicians ensure precise identification of problems, paving the way for effective repairs.
Performing Repairs and Replacements
- Faulty compressors
- Damaged fan motors
- Leaking refrigerant lines
- Broken thermostats
In cases where repairs aren’t feasible or cost-effective, technicians may recommend replacing the entire system with a new unit that meets modern efficiency standards.

Conducting System Upgrades
Modern air conditioning technology continues to evolve rapidly, offering improved energy efficiency and environmental benefits over older systems. As part of their role, HVAC professionals often upgrade outdated units by installing smart thermostats or high-efficiency models designed for better cooling performance.
Delivering Customer Education
- Changing filters regularly (typically every 1–3 months).
- Keeping outdoor units free from debris like leaves or dirt.
- Scheduling annual tune-ups to address wear-and-tear issues proactively.
Educating customers empowers them to care for their systems effectively between service visits.
| Task | Tools Commonly Used | Purpose |
| Diagnostics | Multimeter, gauge manifold | Identify root causes |
| Maintenance | Coil cleaner, lubricants | Enhance system efficiency |
| Repairs/Replacement | Screwdrivers, soldering tools | Restore functionality |
| Upgrades | Smart thermostats | Improve energy savings |
HVAC technicians work diligently every day to ensure homes and businesses stay comfortable year-round through expert care of air conditioning systems while prioritizing safety and efficiency at each step of their workflow.
How a Typical Workday Flows for HVAC Technicians Providing AC Service From Start to Finish
HVAC technicians play a vital role in ensuring that residential and commercial air conditioning systems function smoothly. Their workday often involves addressing various technical challenges, collaborating with clients, and maintaining systems for optimal performance. Here’s an overview of how a typical day unfolds for an HVAC technician working on AC service.
Starting the Day: Preparation and Scheduling
- Reviewing the Schedule: The workday begins with checking the schedule provided by their employer or dispatch system. This includes reviewing the locations, types of service calls, and any specific client notes.
- Gathering Tools and Equipment: Technicians ensure their work vehicles are stocked with essential tools, replacement parts, refrigerants, safety gear, and diagnostic equipment.
- Prioritizing Service Calls: Based on urgency and location, they may prioritize emergency repairs over routine maintenance tasks.
On-Site Arrival: Preliminary Assessment
Upon arriving at a client’s location: – Client Communication: The technician discusses the issue with the client to gain insights into system symptoms or past problems. – Initial Inspection: A visual examination of the unit is conducted to identify obvious issues such as leaks, blockages, or physical damage.
This step helps set the foundation for a more detailed diagnostic process.
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Diagnostics play a critical role in repairing or maintaining AC systems. This phase includes: 1. Testing System Performance: – Measuring airflow levels. – Checking thermostat functionality. – Monitoring refrigerant pressure using gauges. 2. Electrical System Checks: – Inspecting wiring connections. – Testing capacitors and relays using multimeters to locate electrical faults. 3. Mechanical Component Inspection: – Examining compressors, fans, and coils for wear or damage.
Any findings during this process guide decisions about repairs or part replacements.
Performing Repairs or Maintenance
Once diagnostics are complete: – For repair jobs: – Faulty components (e.g., capacitors, motors) are replaced or repaired as needed. – Refrigerant leaks may be sealed followed by recharging to optimal levels. – For maintenance tasks: – Air filters are cleaned or replaced. – Condenser coils are washed to improve efficiency. – Lubrication is applied to moving parts where necessary.
Technicians also test system performance after completing repairs to ensure all issues have been resolved.
Documentation and Reporting
Before leaving a site: – Technicians document all services performed in detail—this can include diagnostic results, repairs made, parts used, and customer recommendations for future upkeep. – They may also provide usage tips or suggest preventive measures such as regular maintenance checks to avoid recurring issues.
Collaboration With Team Members
Throughout their day, HVAC technicians often collaborate with other professionals such as office staff (for scheduling updates), senior technicians (for complex cases), or supply chain teams (to source parts quickly). This teamwork ensures seamless service delivery across all stages of their workflow.
| Time Period | Activity |
| Morning | Reviewing schedule & preparation |
| Mid-morning & Afternoon | Diagnostics & Repair |
| Late Afternoon | Documentation & reporting |
A day in the life of an HVAC technician requires problem-solving skills, attention to detail, technical expertise, and strong communication abilities—all essential traits that ensure customers receive reliable air conditioning services.
How HVAC Technicians Work Together to Complete AC Service Orlando Calls Successfully
The successful completion of an air conditioning (AC) service call requires a collaborative effort among various individuals and teams. HVAC technicians serve as the central figures in this process, utilizing their expertise to diagnose and repair issues, but their effectiveness often hinges on working seamlessly with others. Below, we explore the key stakeholders involved in AC service calls and how their collaboration ensures optimal outcomes.
Key Stakeholders in an AC Service Call
- Dispatchers
Dispatchers play a crucial role in coordinating service calls for HVAC technicians. They: - Schedule appointments based on customer availability and technician workload.
- Provide technicians with essential job details such as customer location, reported issues, and equipment type.
- Act as intermediaries between customers and technicians to address scheduling changes or urgent requests.
- Customers
The collaboration with customers is critical for technicians to deliver satisfactory service. Customers: - Share information about symptoms or performance issues they are experiencing with their AC systems.
- Grant access to the property and any relevant areas such as utility rooms or outdoor units.
- Offer feedback post-service, which helps assess the quality of the work completed.
- Suppliers and Vendors
Technicians frequently rely on suppliers and vendors for parts, tools, or refrigerants necessary for repairs or replacements. This partnership enables technicians to: - Source high-quality replacement components quickly.
- Obtain specialized tools required for diagnostics or complex repairs.
- Stay informed about new equipment models or technologies that may benefit customers.
- Technical Support Teams
In cases where issues are particularly challenging or involve unfamiliar equipment models, HVAC technicians may consult technical support teams provided by manufacturers or distributors. These experts assist by: - Offering guidance on troubleshooting complex problems.
- Recommending appropriate repair methods based on system specifications.
- Clarifying warranty terms if applicable.
- Fellow Technicians
Collaboration among peers is common within larger HVAC companies or during team-based projects like commercial installations. This cooperation allows technicians to: - Share insights gleaned from similar troubleshooting experiences.
- Divide responsibilities when handling extensive repairs involving multiple systems.
- Mentor less experienced colleagues by providing hands-on training.
Collaborative Tools Used by HVAC Technicians
| Tool/Technology | Purpose | Example Use Case |
| Field Service Software | Manages schedules, tracks work orders | Real-time updates about job progress |
| Mobile Communication Apps | Facilitates technician-dispatcher interaction | Quick sharing of photos/videos of system issues |
| Diagnostic Applications | Interfaces with smart systems via Wi-Fi/Bluetooth | Accessing system performance data remotely |
Benefits of Collaboration in AC Service Calls
Effective collaboration ensures that:
– Issues are resolved efficiently without unnecessary delays. – Customers receive clear communication regarding timelines and costs. – Technicians have access to all necessary resources—both human and material—for successful repair.
By fostering a team-oriented approach across various stakeholders, HVAC professionals can deliver top-quality services while maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction.
Expert Orlando, FL AC Repair: The Importance of Diagnostics and System Testing
Diagnostics and system testing are the foundation of professional air conditioning (AC) services. They ensure that HVAC technicians accurately identify problems, optimize system performance, and extend the lifespan of cooling units. Without a systematic approach to diagnosing issues, repairs can be incomplete or ineffective, potentially leading to costlier problems down the road. Here’s an in-depth look at why diagnostics and testing are critical to AC service.
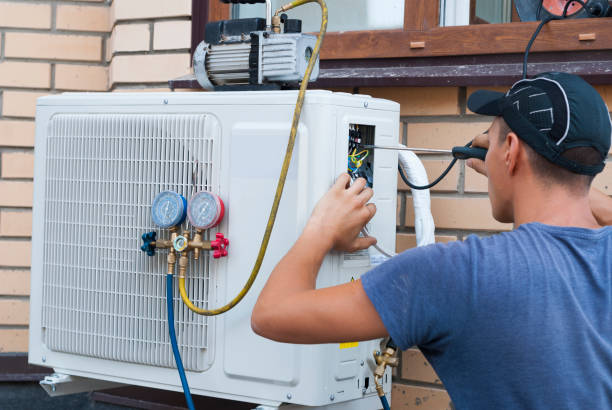
The Purpose of Diagnostics in AC Services
Diagnostics in AC systems is about pinpointing underlying issues rather than just addressing symptoms. A poorly performing air conditioner might show obvious signs like reduced cooling or unusual noises, but these surface-level symptoms could stem from various root causes.
- Identifying inefficiencies: Ensuring the system operates at peak efficiency.
- Preventing breakdowns: Detecting potential failures before they escalate.
- Improving indoor air quality: Addressing issues that compromise filtration or ventilation.
- Saving costs: Reducing energy consumption and minimizing repair expenses.
Tools Used for Diagnostics and Testing
| Tool Name | Purpose |
| Digital Multimeter | Measures voltage, resistance, and current |
| Refrigerant Gauges | Checks refrigerant pressure levels |
| Thermometers | Monitors supply and return air temperatures |
| Leak Detectors | Identifies refrigerant leaks in the system |
| Infrared Cameras | Detects thermal irregularities |
| Manometers | Measures static pressure within duct systems |
Each tool plays a role in gathering precise data about how the system functions under different conditions.
Steps Involved in Diagnostic Procedures
- Assess visible components such as filters, coils, and duct connections for wear or damage.
- Look for physical signs like rusting parts, loose wires, or clogged drains.
- Measure airflow rates to determine if the system delivers adequate cooling.
- Use refrigerant gauges to check operating pressures against manufacturer guidelines.
- Verify voltage levels at key points like capacitors and compressors.
- Test continuity across electrical connections using a multimeter.
- Inspect refrigerant lines for potential leaks using electronic sniffers or bubble solutions.
- Evaluate how well the system cycles on/off under controlled conditions.
- Ensure consistent temperature delivery across all vents.
Benefits of Comprehensive System Testing Post-Service
- Verifying energy efficiency improvements after cleaning or recalibration.
- Ensuring temperature settings align with thermostat readings.
- Confirming there are no residual leaks or electrical hazards post-repair.
Why Skilled Technicians Are Essential
- A drop in refrigerant pressure might indicate a leak but could also result from compressor malfunctions.
- Uneven airflow might point to clogged filters but could also suggest improperly sized ducts.
Skilled technicians combine technical knowledge with hands-on experience to deliver reliable solutions tailored to each unique case.
Proper diagnostics followed by comprehensive testing not only resolves current issues but also safeguards against future malfunctions—keeping your air conditioning unit running smoothly for years ahead.
Understanding the Critical Role of Diagnostics and System Testing in Professional AC Services
Diagnostics and system testing are essential components of professional air conditioning (AC) services, ensuring that systems operate efficiently, reliably, and safely. HVAC technicians rely on these processes not only to identify existing issues but also to prevent potential malfunctions. Let’s explore why diagnostics and testing are critical in AC services and how they contribute to maintaining optimal system performance.
Importance of Diagnostics in AC Services
Proper diagnostics allow HVAC technicians to pinpoint the root cause of a problem rather than addressing symptoms alone. Identifying the underlying issue ensures repairs are effective and reduces unnecessary costs for customers.
- Efficiency: Accurate diagnosis prevents technicians from replacing parts or making adjustments that do not resolve the issue.
- Cost-effectiveness: By identifying the exact fault, homeowners avoid unnecessary expenses on incorrect repairs.
- System longevity: Diagnosing minor issues early helps prevent them from escalating into costly, long-term damage.
- Safety assurance: Proper diagnostics ensure that issues such as refrigerant leaks or electrical faults are addressed promptly, reducing hazards.
Core Diagnostic Techniques Used by HVAC Professionals
- Examining components like filters, coils, wiring, and fan motors for visible signs of wear or damage.
- Checking for loose connections or external blockages that may hinder proper operation.
- Measuring voltage levels at key points within the system to detect malfunctions such as faulty capacitors or broken relays.
- Using gauge sets to measure refrigerant levels and pressures within the unit.
- Identifying leaks or imbalances in refrigerant charge, which can severely impact cooling efficiency.
- Detecting temperature inconsistencies across various system parts to uncover hidden issues like overheating components.
- Monitoring airflow rates using devices such as anemometers or flow hoods ensures adequate ventilation through ducts.
System Testing During Routine Maintenance
| Test Type | Purpose |
| Thermostat Calibration | Ensures temperature settings align with actual room conditions |
| Air Filter Inspection | Verifies proper airflow by replacing clogged or dirty filters |
| Condenser Coil Check | Confirms heat exchange efficiency by inspecting coil cleanliness |
| Performance Metrics | Measures cooling capacity and energy consumption under load conditions |
| Safety Controls | Tests safety mechanisms like high-pressure cutoffs for reliability |
Benefits of Diagnostics and System Testing for Customers
- Enhanced energy efficiency leads to lower utility bills.
- Extended equipment lifespan reduces the need for frequent replacements.
- Increased comfort due to consistent cooling performance.
- Peace of mind knowing potential hazards are identified early.
Diagnostics and system testing form the backbone of professional AC maintenance services. By dedicating time to thorough evaluations, HVAC technicians ensure every air conditioning unit operates at peak performance while providing customers with lasting value.
- Timely AC Service Orlando: Why Regular Maintenance and Repairs Matter
- Top Signs You May Need Air Conditioning Repair Orlando, FL Immediately
- Ensuring Year-Round Home Comfort with Reliable AC Service Orlando
- Detailed Guide to Air Conditioning Repair Orlando, FL: Top 6 Common Problems and Solutions
- How to Tell When You Need an AC Service Orlando Specialist for a Replacement
- General Recommendations for AC Service
- 5 Key Signs Your AC Service Orlando Home Needs Immediate Repair or Cleaning
- Common Orlando, FL AC Repair Issues and How to Resolve Them